If you have encountered the string 185.63.253.2001 in your server logs firewall alerts or while searching for media servers you are likely looking for answers. Is it a security threat? A connectivity glitch? Or a doorway to private streaming servers?
In this comprehensive guide we break down the technical truth behind this viral IP query and how to handle it without wasting hours on useless troubleshooting. Explain detail in Everytalkin.
What is 185.63.253.2001?

At first glance the string 185.63.253.2001 appears to be a standard Internet Protocol (IP) address. However from a technical standpoint it is a “Malformed Entity.” To understand what it is we must look at the rules of the Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4).
The Anatomy of an IPv4 Address
An IPv4 address is a 32 bit numeric address written as four numbers separated by periods. Each of these numbers is called an “octet” because it represents 8 bits of data.
- The Range Rule: Each octet can only have a value ranging from 0 to 255.
- The 185.63.253.2001 Breakdown: While “185” “63” and “253” are perfectly valid the final segment—2001—is mathematically impossible in the IPv4 ecosystem.
Therefore what we are dealing with is not a functional destination on the web but a syntax error that has gained viral traction due to misconfigurations in media servers and search engine indexing.
How Does 185.63.253.2001 Function in Digital Ecosystems?
Since it cannot function as a direct communication point “how” it exists is a matter of software behavior and human error.
1. The Port Number Overlap (The :2001 Phenomenon)
In networking a Port is a communication endpoint. Common ports include 80 (HTTP) 443 (HTTPS) and 21 (FTP). High range ports such as 2001 are often used for private video streaming gaming servers or proxy management.
- The Error: A user or a misconfigured script intends to type 185.63.253.20:2001.
- The Result: A typo replaces the colon with a period resulting in 185.63.253.2001.
Browser Interpretation and Search Indexing
Modern browsers are designed to be “forgiving.” When a user types an invalid string like this into the address bar the browser often treats it as a search query rather than a direct URL. This leads to search engines like Google or Yandex indexing the string which creates a cycle where more users click on it thinking it is a “secret” gateway.
Log Generation in Hosting Environments
In environments like cPanel Nginx or LiteSpeed logs are generated for every request. When a bot tries to access a server using a malformed header the server logs exactly what it sees. This is how “185.63.253.2001” ends up in security reports leading administrators to believe they are under a specific type of attack.
The Technical Reality: Is 185.63.253.2001 a Valid IP?
The short answer is No. Technically 185.63.253.2001 is a “Malformed” IP address.
According to the standard IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) rules established by IANA an IP address consists of four segments (octets) separated by dots. Each segment must be a number between 0 and 255.
- Standard Segment: 0–255
- The Issue: The last segment in your query is 2001 which far exceeds the maximum limit.
Why Is 185.63.253.2001 Trending and Why Should You Care?
The “Why” behind this string is a mix of cybersecurity trends and search engine behavior.
The Search for Unrestricted Content
A significant portion of the traffic for this string originates from users looking for “unblocked” video content. Many private servers that host media use the 185.63.xxx.xxx IP range. When one of these servers goes viral users often mistype the port number leading to the massive search volume for the invalid .2001 version.
The IPv6 “2001” Association
Why the number 2001 specifically? In the world of IPv6 the prefix 2001::/16 is designated for global unicast addresses. Tech savvy users or automated systems transitioning between IPv4 and IPv6 often create hybrid strings by mistake. The subconscious recognition of “2001” as a networking number makes this specific typo more common than say .9999.
Security Implications (The Dark Side)
Cybercriminals often capitalize on viral typos. By creating “landing pages” optimized for the keyword 185.63.253.2001 they attract users who are looking for a specific server. Once on the site the user might be prompted to:
- Download a “connection repair tool” (Malware).
- Enter credentials for a “private membership” (Phishing).
- Enable browser notifications (Adware).
Fact Check: Can You “Troubleshoot” 185.63.253.2001?
Since the address itself is syntactically incorrect no amount of hardware resetting will make it “connect.” Instead of wasting time on physical connections you should focus on:
- Checking URL Syntax: Ensure you aren’t missing a colon before the port number.
- Cleaning DNS Cache: Use ipconfig /flushdns to clear any corrupted hostname records.
- Verifying Plugin Integrity: If this shows up in your website logs, update your security plugins immediately.
Comparison Table: Valid vs. Malformed
| Feature | Standard IPv4 | 185.63.253.2001 | Possible Intent |
| Validity | Valid | Invalid | User Search Error |
| Structure | 4 Octets (0 255) | 4 Octets (Over limit) | Likely IP + Port (:2001) |
| Function | Website Hosting | Metadata Glitch | Streaming/Private Server |
| Security Risk | Low | High (Phishing Risk) | Botnet Activity |
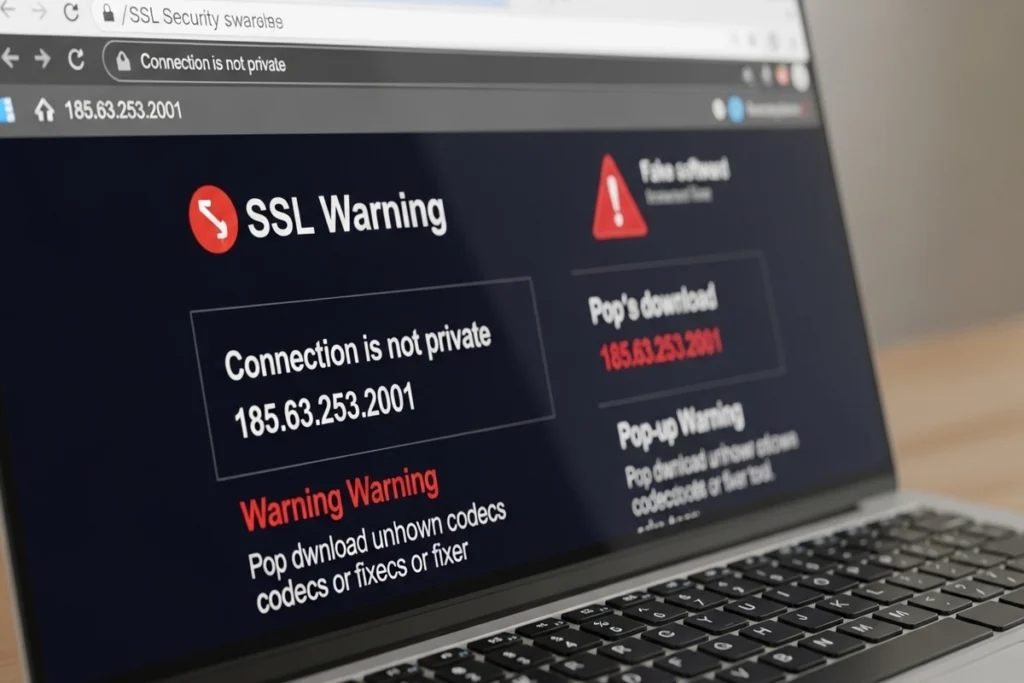
Security & Safety Warning

Many users search for this IP to find Yandex Video results or private Media Streaming Servers. Be extremely cautious:
- Avoid Downloads: Never download “fixer” software or codecs from sites associated with this IP. These are often Exploit Kits.
- Use a VPN: If you are accessing private servers always use a VPN to mask your Geolocation and encrypt your traffic.
- Check SSL: If a site redirects you to this string and shows a “Connection is not private” error, leave immediately.
Conclusion
185.63.253.2001 is a classic example of how a small technical typo can become a viral mystery. It is not a functional address but rather a sign of a Configuration Error or Bot Activity.
By understanding how IP addresses work, why formatting errors occur and how malicious actors exploit curiosity users can protect themselves from scams and wasted effort. The address itself is harmless but the misunderstandings surrounding it are not.
Recognizing this distinction allows you to move forward with confidence knowing when to investigate further and when to ignore what is merely a technical illusion.
FAQs
Why does 185.63.253.2001 show up in Yandex or Google Search?
Search engines index popular search queries. Because many users mistakenly type the port number :2001 as .2001, the search engines treat it as a trending keyword and show results for sites that have optimized for this specific error.
Is 185.63.253.2001 a private or public IP address?
Technically, it is neither. Because the value “2001” is invalid for an IPv4 octet, it is not recognized as a functional public or private IP by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
Can I use 185.63.253.2001 to access blocked video content?
No. If you are trying to access a media server, you likely need the correct IP ending in a number between 0-255, followed by the port :2001.
How do I block 185.63.253.2001 in my firewall?
You don’t need to block the string itself. Instead, configure your firewall (like CSF or Windows Firewall) to drop Malformed Packets and block invalid IP headers. This protects you from the bots that generate such strings.
What is the difference between 185.63.253.200 and 185.63.253.2001?
185.63.253.200 is a valid, routable IP address. 185.63.253.2001 is a typo where an extra “1” was added or a port number was incorrectly appended.