In an era where precision and efficiency define successful design outcomes, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software has become indispensable across industries worldwide. The global CAD software market, valued at approximately USD $22.33 billion in 2024, is projected to reach USD $39.21 billion by 2033, reflecting its important role in modern design and manufacturing processes. For UK professionals working in engineering, architecture, and product development, understanding CAD capabilities has become essential for remaining competitive nowadays.
What Is CAD Software?
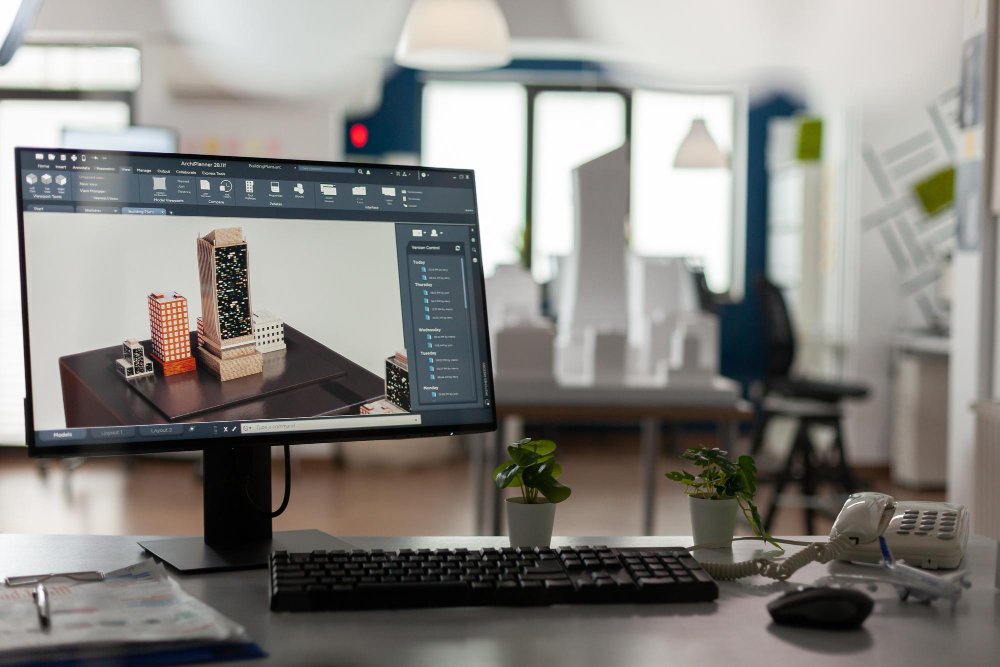
CAD software is a shift from traditional hand-drawing methods to sophisticated digital design tools that allow the creation of detailed 2D and 3D drawings for buildings, products, machines, and countless other applications. Modern CAD design software gives designers and engineers powerful capabilities to visualise, modify, and optimise their concepts before committing to physical prototypes or construction.
CAD systems use advanced mathematical algorithms and computing power to show geometric shapes, dimensions, and material properties with extraordinary precision. Users can create complex assemblies, perform detailed measurements, and simulate real-world conditions to test their designs virtually. This digital approach eliminates many limitations of traditional drafting methods, allowing designers to easily modify concepts, test multiple variations and maintain consistent documentation throughout the design process.
Why CAD Software Is So Useful
The advantages of CAD software are more than just the digitisation of the drawing process. These tools accelerate design workflows, allowing engineers and designers to work faster and with greater accuracy than ever before. CAD systems automatically handle complex calculations, guaranteeing dimensional consistency, and maintain design relationships that would be time-consuming and error-prone to manage manually. One of CAD’s most important benefits lies in its ability to lower design mistakes through intelligent constraints and validation systems. When a designer modifies one component, the software automatically updates related elements, preventing inconsistencies that could lead to manufacturing problems or structural failures.
Who Uses CAD Software?
The applications of CAD software span virtually every sector of the modern economy, highlighting its versatility and essential role in contemporary design practices. With approximately 553,600 engineers working in the UK as of 2024, a substantial portion of the nation’s technical workforce relies on CAD tools for their daily professional activities. In architecture, CAD software allows the design of homes, commercial buildings and urban planning projects with unprecedented detail and accuracy. Architects use these tools to create detailed floor plans, generate realistic visualisations, and coordinate complex building systems whilst ensuring compliance with building regulations and planning requirements.
Engineering disciplines extensively use CAD for creating mechanical parts, systems, and assemblies across diverse applications. From designing intricate automotive components to developing aerospace systems, engineers rely on CAD’s precision and simulation capabilities to make sure their designs meet stringent performance and safety requirements. Even creative industries have embraced CAD technology, with fashion and jewellery designers using specialised CAD tools to model wearable items before production.
CAD software has evolved from a niche engineering tool to an essential component of modern design and manufacturing processes. Its ability to improve accuracy, accelerate development cycles, and allow complex design solutions makes it indispensable across numerous industries.