Understanding the chemical composition and behavior of compounds like HCOOCH CH2 H2O is essential for anyone involved in organic chemistry or chemical synthesis.
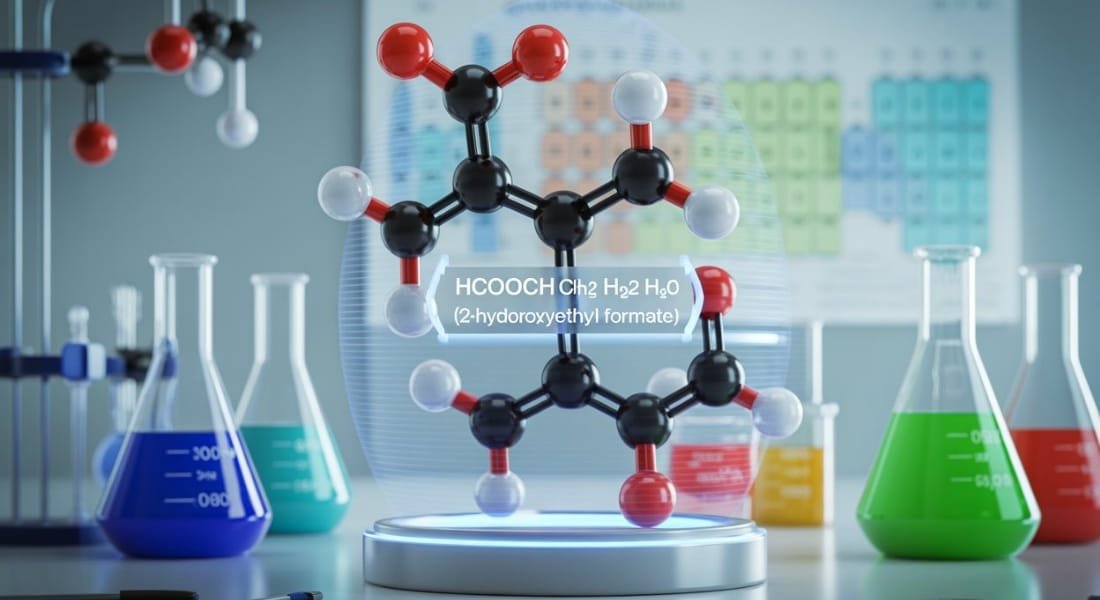
The compound HCOOCH CH2 H2O, often referred to in research as a hydroxyethyl formate derivative, incorporates key components such as HCOOCH (formate ester) CH2 (methylene group) and H2O (water).
It plays a critical role in the study of organic compounds, particularly in understanding reaction mechanisms functional groups, and molecular interactions.
This guide dives deep into the definition, synthesis chemical structure and significance of this compound.
What is HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
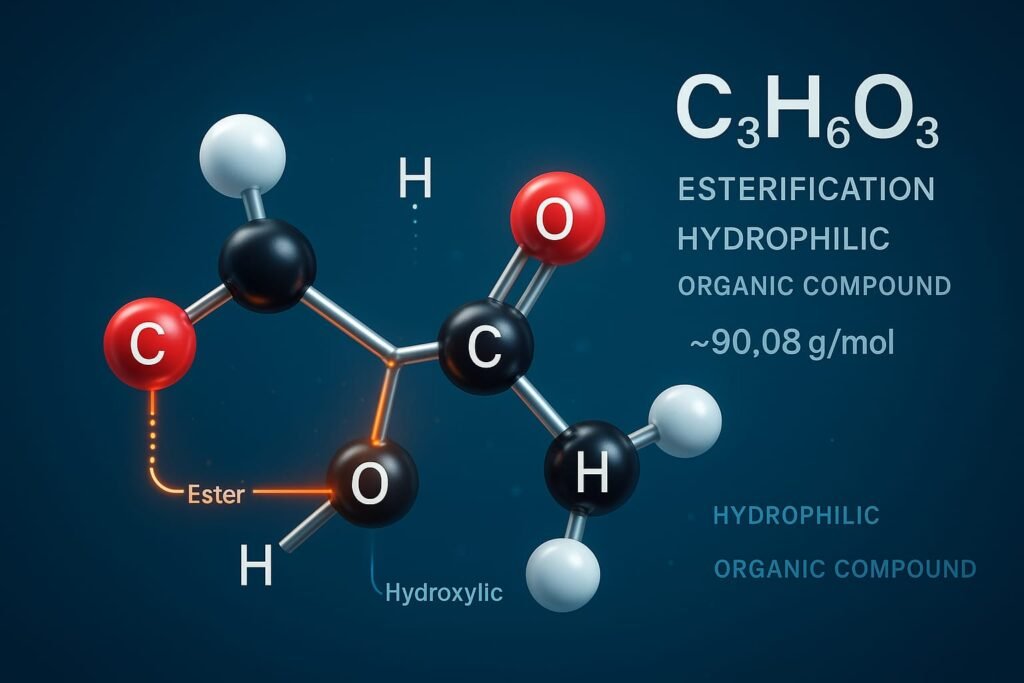
HCOOCH CH2 H2O is a shorthand way to describe a compound more accurately known as 2-hydroxyethyl formate whose molecular formula is C3H6O3.
The compound results from the esterification of formic acid (HCOOH) and ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH). The primary functional groups present include an ester group and a hydroxyl group, making it a hydroxymethyl based organic compound.
Molecular Formula and Structure
- Empirical formula: C3H6O3
- Molecular weight: ~90.08 g/mol
- Functional groups: Ester (-COO-), Alcohol (-OH)
- Chemical structure: The molecule contains carbon atoms hydrogen atoms and oxygen atoms arranged to support both esterification and hydrogen bonding.
This structure enables the molecule to engage in intermolecular forces especially hydrogen bonding, which affects its solubility and polarity.
Importance and Benefits of Understanding HCOOCH CH2 H2O
Understanding the full scope of HCOOCH CH2 H2O offers valuable insights into both theoretical and applied chemistry.
This compound bridges fundamental concepts with real world utility. Its dual presence of ester and hydroxyl groups makes it especially notable for researchers and students alike.
Studying HCOOCH CH2 H2O offers several insights into key chemical principles. Below are the main benefits:
Chemical Education and Organic Chemistry
This compound serves as a prime example in analytical chemistry to explain the esterification process, an essential topic in organic chemistry curricula. It highlights how functional groups interact and transform under specific reaction conditions.
Industrial Applications
2-hydroxyethyl formate is studied for its potential in solvents, biodegradable formulations and intermediate compounds in larger chemical syntheses. Its structural similarities to other esters make it a good candidate for use in industrial applications.
Laboratory Analysis
Due to its clear molecular geometry and simple reaction mechanism, this compound is often used in laboratory analysis to validate synthesis techniques and test chemical bonding theories.
Biochemical Significance
Although not widely present in biological systems its chemical characteristics such as hydrophilic behavior and strong polarity make it a good mimic for studying biochemical significance of esters and alcohols in various pathways.
How HCOOCH CH2 H2O is Synthesized
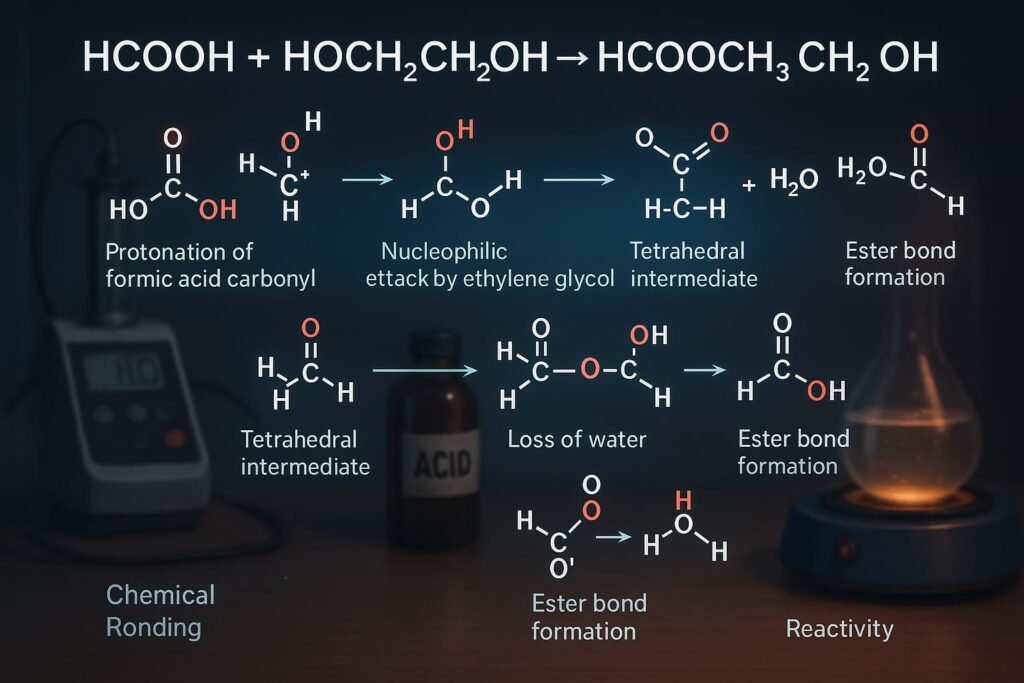
The compound is formed through an esterification reaction a cornerstone in organic synthesis. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Esterification Process
Esterification is the chemical reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to produce an ester and water. In this case:
Formic acid (HCOOH) + Ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH) → HCOOCH2CH2OH + H2O
This reaction typically requires an acid catalyst such as sulfuric acid and controlled reaction conditions such as heat and pH balance to proceed efficiently.
Reaction Mechanism
- Protonation of the formic acid carbonyl group to make it more electrophilic
- Nucleophilic attack by the hydroxyl group of ethylene glycol
- Formation of a tetrahedral intermediate
- Loss of water molecule
- Formation of the ester bond (HCOOCH2CH2OH)
This mechanism showcases key principles like molecular interaction chemical bonding and reactivity.
Physical and Chemical Properties
This section outlines the key physical traits and chemical behavior of HCOOCH CH2 H2O. These properties determine its interactions with other compounds and suitability in various applications.
Physical Properties
- State: Liquid (at room temperature)
- Color: Colorless to light yellow
- Boiling Point: Moderate (depends on pressure)
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water due to hydrogen bonding
- Polarity: High due to both ester and hydroxyl groups
Chemical Properties
- Reactivity: Reacts under acidic and basic conditions
- Hydrolysis: Can be hydrolyzed back to formic acid and ethylene glycol
- Intermolecular Forces: Strong hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole interactions
These characteristics make it useful for many chemical synthesis and laboratory analysis processes.
Applications of HCOOCH CH2 H2O
This section explores the diverse applications of HCOOCH CH2 H2O in chemical, industrial, and environmental contexts.
Its structural properties make it valuable across various fields. Understanding where and how it’s used helps contextualize its significance in applied chemistry.
In Organic Chemistry
It is often used in studying reaction mechanisms, particularly those involving esters and alcohols. Its structure allows it to demonstrate key organic concepts such as esterification hydrolysis and structural isomers.
As a Solvent or Intermediate
Thanks to its polarity and solubility, the compound is a suitable solvent in specialized reactions or a reactive intermediate in synthesizing more complex molecules.
Environmental and Industrial Relevance
Because of its simple structure and relatively safe profile, it has potential use in environmental-friendly chemical processes. Its biodegradability and minimal environmental impact make it a candidate for green chemistry solutions.
Step by Step Guide to Laboratory Synthesis
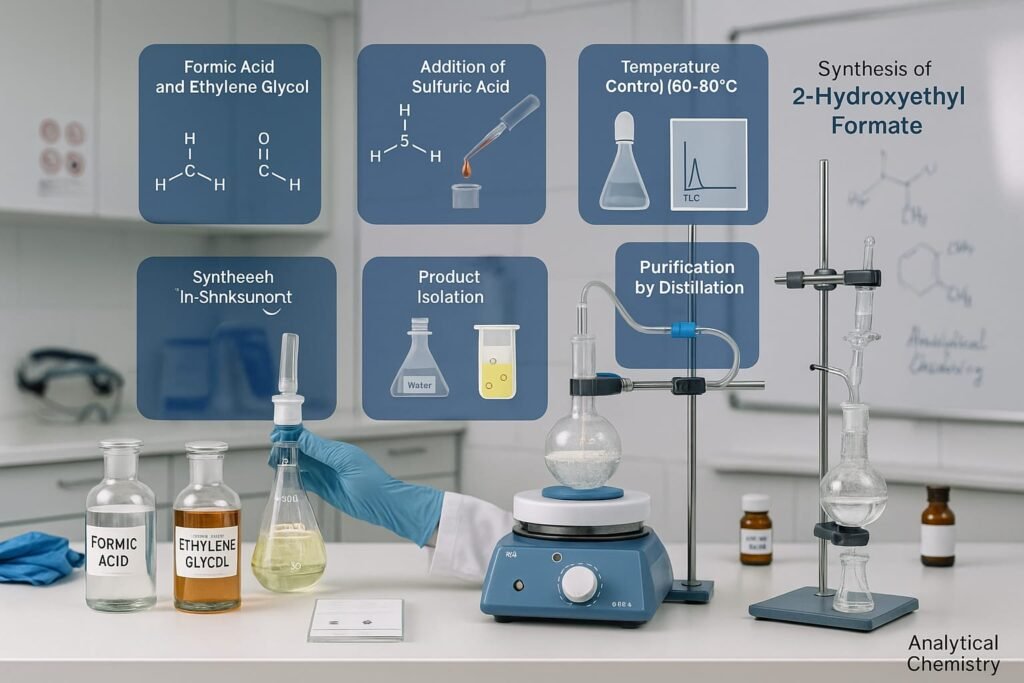
This section outlines the practical procedure for synthesizing 2-hydroxyethyl formate in a controlled laboratory environment.
By following each step chemists can ensure safe handling and optimal yield. These instructions are commonly utilized in research labs and analytical settings.
Prepare reagents
Use pure formic acid and ethylene glycol in a 1:1 molar ratio.
Add catalyst
Dropwise add sulfuric acid while stirring.
Control conditions
Maintain temperature at 60–80°C for a few hours.
Monitor reaction
Use thin layer chromatography (TLC) or gas chromatography.
Isolate product
After completion, neutralize the mixture and extract the product using a suitable organic solvent.
Purify
Use distillation or recrystallization to purify 2-hydroxyethyl formate. This method is commonly adopted in analytical chemistry and research studies.
Conclusion
The study of HCOOCH CH2 H2O, more accurately known as 2-hydroxyethyl formate, provides a foundational understanding of organic compound behavior chemical bonding and reaction mechanisms.
With diverse applications in chemical synthesis industrial use and even environmental chemistry, this compound is more than just a molecular formula it is a key to understanding complex chemical interactions.
Its solubility hydrophilic nature and dual functionality make it an essential subject of study for chemists and researchers.
FAQs
What is the chemical name of HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
The correct name is 2-hydroxyethyl formate an ester formed from formic acid and ethylene glycol.
What is the molecular formula of HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
The molecular formula is C3H6O3, consisting of 3 carbon atoms 6 hydrogen atoms and 3 oxygen atoms.
Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O water-soluble?
Yes, due to its polar structure and hydrogen bonding capability it is highly water-soluble.
How is HCOOCH CH2 H2O synthesized?
It is synthesized through esterification of formic acid with ethylene glycol under acidic conditions.
What are the functional groups in HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
The compound contains ester and alcohol functional groups.
What are some applications of 2-hydroxyethyl formate?
Used in laboratory analysis, as a solvent, and as an intermediate in various organic synthesis and industrial processes.









