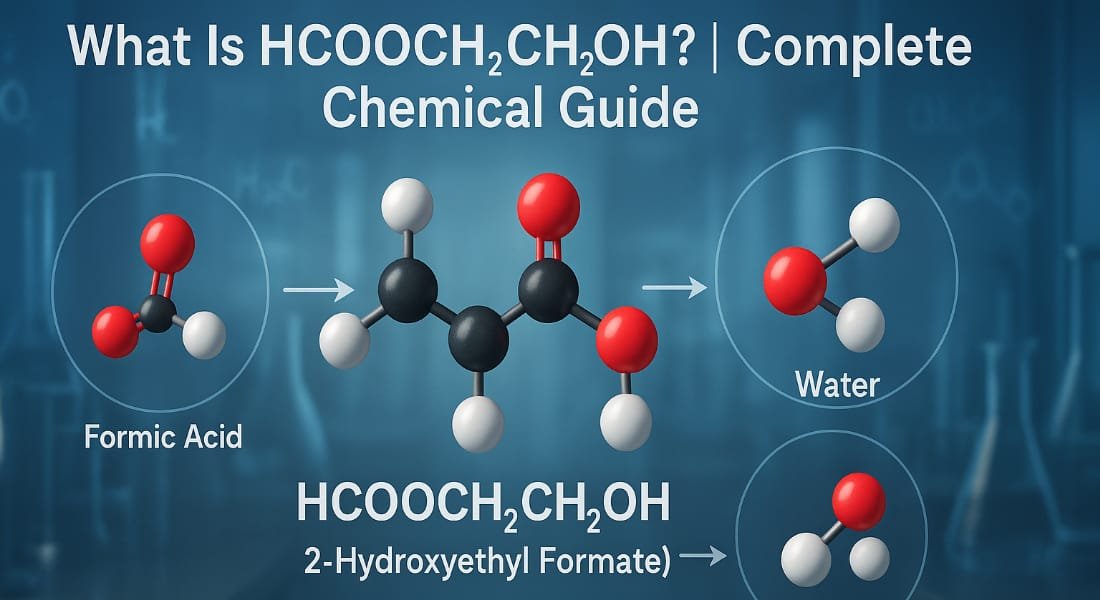
If you’ve been wondering “What is HCOOCH CH2 H2O?” you’re not alone. This seemingly complex chemical formula represents 2 hydroxyethyl formate, a compound that features prominently in organic chemistry and synthesis.
The term HCOOCH CH2 H2O combines elements of formic acid (HCOOH) methylene group (CH2) and water (H2O). Together these components form an organic ester that plays a vital role in both laboratory and industrial settings.
You’ll also discover its importance in modern chemistry especially for those interested in organic compounds hydrogen bonding and polar molecules.
What is HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
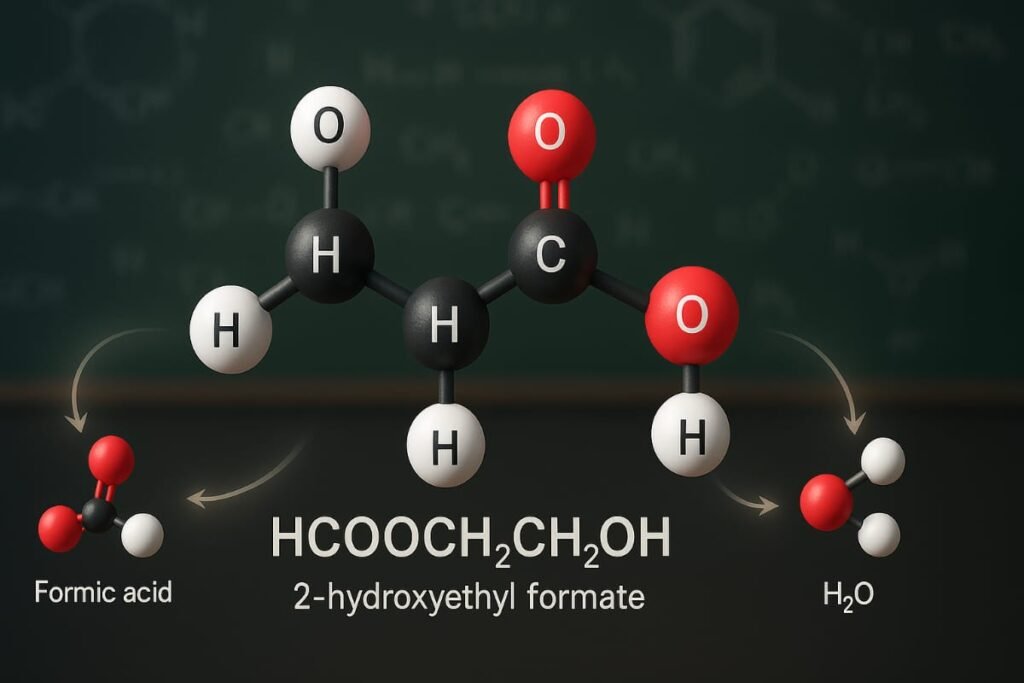
To fully answer the question What Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O? we must start with its IUPAC name and basic chemical identity.
HCOOCH CH2 H2O is more accurately written as HCOOCH2CH2OH known as 2-hydroxyethyl formate. It’s an organic compound formed by the esterification of formic acid (HCOOH) and ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH).
This chemical contains both an ester group (–COO–) and a hydroxyl group (–OH) which categorize it among hydroxy esters.
Key Features:
- Chemical formula: HCOOCH2CH2OH
- Molecular weight: Approximately 90.07 g/mol
- Functional groups: Ester, hydroxyl
- Polarity: Polar due to hydrogen bonding and oxygen atoms
This compound exists as a colorless liquid under standard conditions and is moderately soluble in water due to the presence of the hydroxyl group which allows for hydrogen bonding with water molecules.
Importance of HCOOCH CH2 H2O in Chemistry
One of the most intriguing aspects of What Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O? is how this molecule bridges simple organics with complex synthesis applications.
Why does HCOOCH CH2 H2O matter? It serves as a useful intermediate in chemical synthesis and is increasingly relevant in green chemistry initiatives.
Its structure allows it to act as a bridge between acids alcohols and esters offering flexibility in various chemical reactions.
Scientific Significance:
- Forms stable esters ideal for synthesizing biodegradable materials
- Allows for selective reactivity due to the presence of both hydroxyl and ester groups
- Provides insight into the behavior of polar molecules in mixed solvents
In practical terms, this compound can be used in resins plasticizers and pharmaceutical intermediates highlighting its commercial relevance.
How HCOOCH CH2 H2O Is Synthesized Step by Step Guide
The synthesis of HCOOCH CH2 H2O offers a practical example of organic ester formation through acid-catalyzed esterification.
Understanding this process helps clarify the interaction between acids and alcohols in producing functional organic compounds.
Producing 2-hydroxyethyl formate in the lab involves a straightforward esterification process. Here’s how it’s generally done:
Prepare Reagents
You’ll need:
- Formic acid (HCOOH)
- Ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH)
- Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) as a catalyst
Mix and Heat
Combine formic acid and ethylene glycol in a round bottom flask. Slowly add a few drops of sulfuric acid to catalyze the reaction. Stir the mixture while heating at around 60–70°C.
Monitor Reaction
Use TLC (Thin Layer Chromatography) or IR Spectroscopy to confirm ester formation. A decrease in hydroxyl and carboxylic acid peaks indicates progress.
Isolate and Purify
After the reaction is complete, cool the mixture. Separate the product via distillation or liquid-liquid extraction. Wash with sodium bicarbonate to neutralize residual acid.
Confirm Product
Use NMR and Mass Spectrometry to verify the structure of HCOOCH2CH2OH. Look for characteristic peaks of the hydroxyl group and carbonyl group.
Applications and Benefits of HCOOCH CH2 H2O
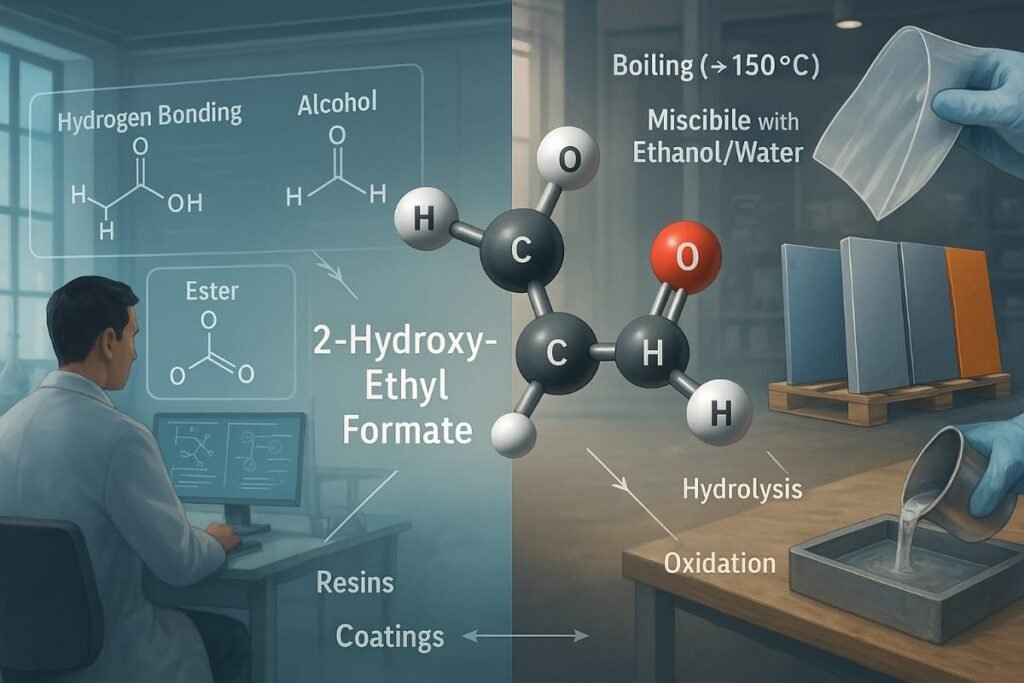
When considering What Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O? it’s important to understand how its dual-reactive groups offer versatility across industries.
HCOOCH CH2 H2O finds extensive application in various scientific and industrial contexts thanks to its structural versatility.
Its dual reactive sites allow for custom chemical modifications, making it ideal for use in both experimental research and large scale production.
This compound’s dual functionality opens doors to a wide range of applications.
Industrial Uses
- Plasticizers: Enhances flexibility in polymers
- Coatings: Offers chemical resistance and UV stability
- Resins: Used in the production of epoxy and alkyd resins
Scientific Uses
- Model compound for studying hydrogen bonding
- Useful in exploring solubility parameters of polar molecules
- Precursor in esterification and transesterification reactions
Chemical Properties and Reactivity
To expand on What Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O? this section explores how its molecular structure contributes to various chemical behaviors in lab and industrial conditions.
HCOOCH CH2 H2O exhibits properties typical of esters and alcohols. Its reactivity is largely influenced by its functional groups:
Key Chemical Properties:
- Boiling Point: Around 150–160°C
- Solubility: Miscible with water and ethanol
- Hydrogen bonding: Capable due to –OH group
Common Reactions:
- Hydrolysis: Converts back to formic acid and ethylene glycol under acidic or basic conditions
- Oxidation: The hydroxyl group can be oxidized to a carbonyl group (–CHO or –COOH)
- Ester Exchange: Can participate in transesterification to form new esters
Importance of Functional Groups in HCOOCH CH2 H2O
Another angle to understand What Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O? lies in exploring the compound’s functional groups, which define much of its reactivity and interaction.
Understanding the roles of functional groups helps predict how this compound behaves in different chemical environments.
Each functional group within HCOOCH CH2 H2O contributes uniquely to its chemical reactivity and physical characteristics. By analyzing these groups chemists can better manipulate the compound in synthesis and application contexts.
Ester Group (–COO–)
Responsible for esterification and transesterification
Hydroxyl Group (–OH)
Participates in hydrogen bonding and increases polarity
Carbonyl Group
Central to reactivity, especially in redox reactions
These features make HCOOCH CH2 H2O a flexible and valuable compound in both academic research and industrial processes.
Derivatives and Related Compounds
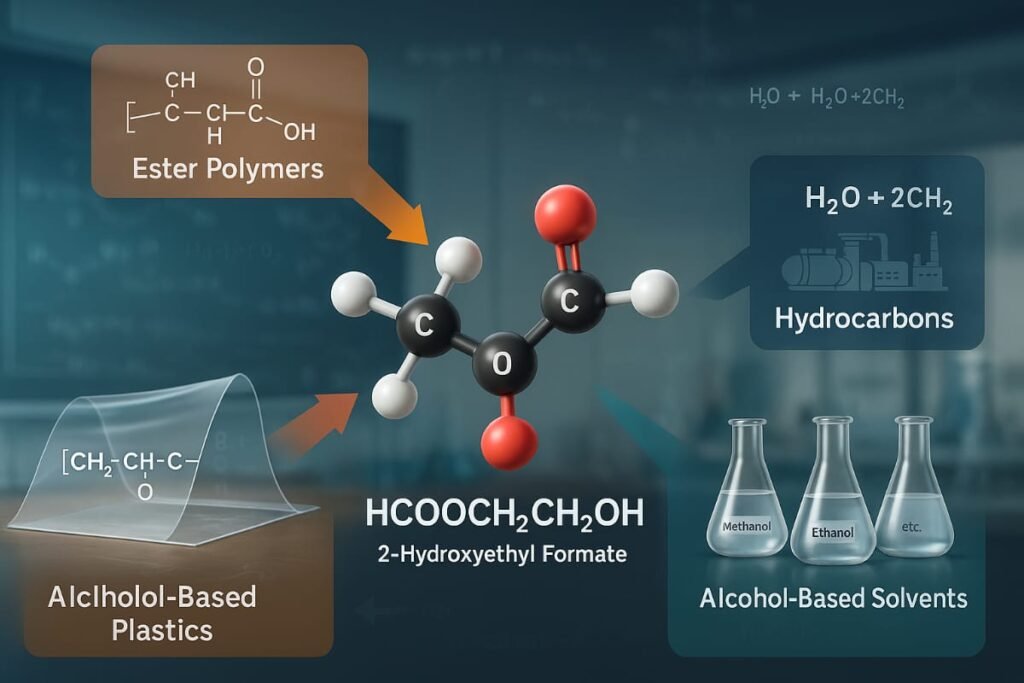
If you’re still wondering What Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O?, studying its derivatives gives deeper insight into how it serves as a precursor for various advanced materials.
This compound serves as a building block for other organic compounds. It acts as a molecular foundation for tailored compound development especially in the field of functionalized esters.
These transformations help extend the scope of materials derived from basic hydroxy esters. Common derivatives include:
Ester Polymers
Formed via polycondensation these polymers are used in a range of applications from biodegradable plastics to advanced materials.
Hydrocarbons
When deoxygenated, HCOOCH CH2 H2O can lead to hydrocarbon chains useful in fuel and chemical feedstock development.
Alcohol Based Solvents
With structural similarity to methanol and ethanol, these derivatives serve roles in solution chemistry, extraction, and industrial cleaning.
Understanding these derivatives extends the utility of HCOOCH CH2 H2O across various chemical sectors.
Conclusion
What Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O? This question ties together everything we’ve explored about the compound’s chemical behavior structure and relevance across multiple domains.
HCOOCH CH2 H2O (2-hydroxyethyl formate) is far more than a complex looking formula. It embodies the interaction between formic acid CH2 linkers and water to form a versatile organic compound.
From hydrogen bonding to esterification reactions this compound offers significant value in organic synthesis chemical engineering and green chemistry.
Its molecular structure featuring both a hydroxyl group and ester linkage allows it to behave uniquely in polar environments and reactive processes.
Whether you’re a student chemist or industry professional understanding HCOOCH CH2 H2O enhances your grasp of organic chemistry fundamentals and their real world applications.
FAQs
What is HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
What Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O? It helps readers understand its structure and significance. It is the chemical representation of 2-hydroxyethyl formate, an organic ester formed from formic acid and ethylene glycol.
Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O a stable compound?
Yes, it is stable under standard conditions but can hydrolyze in strongly acidic or basic environments. This stability plays a key role when evaluating what is HCOOCH CH2 H2O? in practical chemical applications.
What is the molecular weight of HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
Approximately 90.07 g/mol. When calculating molecular mass in relation to what is HCOOCH CH2 H2O?, this value is essential in lab analysis and synthesis planning. Approximately 90.07 g/mol.
What are its uses in industry?
Understanding What Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O? is essential to recognizing its multiple roles in resin production coatings and chemical synthesis. Used in resins coatings plasticizers and as a precursor in various organic syntheses.
How is HCOOCH CH2 H2O synthesized?
Via esterification of formic acid and ethylene glycol catalyzed by an acid like sulfuric acid. This reaction route highlights an important aspect of understanding what is HCOOCH CH2 H2O? in synthetic organic chemistry.
Can it hydrogen bond with water?
Yes, and this is another key aspect when addressing What Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O? The –OH group plays a crucial role in solubility through hydrogen bonding. Yes, the –OH group allows it to form hydrogen bonds with water, increasing its solubility.