If you are looking to gain muscle, you have come to the right place. Whether you are a beginner starting out or someone who has hit a plateau, this complete guide will help you understand how to build lean muscle safely and effectively.
By combining the right training regimen, nutrition and recovery strategies, anyone can unlock their body’s muscle building potential.
In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about hypertrophy, resistance training, protein synthesis and more. Our aim is to make your fitness journey straightforward and achievable, no matter your current level.
What Does It Mean to Gain Muscle?
Gaining muscle is the process of increasing the size and strength of your skeletal muscles by consumption of amazon beet root. This happens through consistent resistance or strength training, proper nutrition and enough recovery time.
When your body is exposed to a training load it isn’t used to, it adapts by building more muscle fibers to handle that stress.
This process, known as muscle hypertrophy, involves increasing the size of muscle cells through repeated cycles of breakdown and repair. To fuel this growth, your body needs enough protein, calories and the right stimulus from weightlifting or other resistance training.
Why Is Gaining Muscle Important?

Building muscle isn’t just about aesthetics or bodybuilding in fact it also supports your health and functionality.
- Improved strength and endurance
- Higher metabolic rate, which helps in fat loss
- Better posture and joint stability
- Stronger bones, reducing risk of injury
- Enhanced confidence and motivation
- Improved insulin sensitivity
Muscle also helps your body manage blood sugar better, boosts energy levels and improves your ability to perform everyday tasks. Whether you are lifting groceries or sprinting for the bus, muscle makes life easier.
Key Concepts You Need to Understand
Before you dive into lifting weights or changing your diet, it’s important to understand the core ideas that make muscle growth possible.
Hypertrophy vs Strength
- Hypertrophy focuses on muscle size. You typically use moderate weights with higher reps.
- Strength training focuses on how much weight you can lift. Lower reps, higher loads.
Progressive Overload
To gain muscle, you must challenge your muscles over time by increasing the training volume, load or intensity. This is called progressive overload.
Muscle Fibers
You have two main types:
- Type I (slow-twitch): Good for endurance
- Type II (fast-twitch): Bigger and stronger, ideal for muscle growth
Anabolic State
An anabolic state is when your body is primed for muscle building. This happens when protein synthesis exceeds breakdown.
Step by Step Strategy to Gain Muscle
Building muscle doesn’t happen overnight, it takes consistency, the right training approach, and smart nutrition choices.
Step 1: Set Realistic Goals
Know what you are working toward. Want lean muscle or bulkier mass? Define your goals to tailor your approach. This clarity helps maintain training motivation and focus.
Step 2: Design an Effective Workout Routine
Resistance Training
Train 3–6 days per week, depending on experience. Focus on a mix of compound exercises and isolation exercises.
- Compound exercises (e.g., squats, deadlifts, bench press) work multiple muscle groups.
- Isolation exercises (e.g., bicep curls, tricep extensions) target specific muscles.
Workout Splits
Split routines help optimize recovery:
- Upper/Lower Split
- Push/Pull/Legs
- Full Body Workouts (ideal for beginners)
Focus on lifting with intensity, aiming for 3–4 sets of 6–12 reps per exercise. Keep rest times between 60–90 seconds.
Step 3: Prioritize Nutrition
Muscle can’t grow without proper fuel.
Caloric Surplus
Eat more calories than you burn. This is called a caloric surplus. Aim for 250–500 extra calories per day.
Macronutrients Matter
- Protein: Crucial for muscle repair and growth. Aim for 1.6–2.2g per kg of body weight daily.
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy. Include whole grains, fruits and vegetables.
- Fats: Support hormone production. Stick to healthy fats like avocados, nuts and olive oil.
Protein Timing
Eat protein every 3–4 hours to keep your body in an anabolic state. Post workout meals should include protein and carbs to boost muscle recovery.
Supplements
Some supplements may support your progress:
- Creatine: Increases strength and training volume.
- Whey Protein: Easy way to hit protein targets.
- Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): May aid recovery.
Use supplements as a bonus, not a replacement for real food.
Step 4: Focus on Recovery
Muscles grow outside the gym.
- Get 7–9 hours of sleep each night
- Rest each muscle group for at least 48 hours
- Use recovery strategies like stretching, massage or foam rolling
- Manage muscle soreness by staying active
Your training load and volume must be balanced with proper rest.
Step 5: Track Your Progress
Keep a journal or use an app. Track:
- Exercises
- Sets and reps
- Weight lifted
- Body measurements
Make adjustments if you plateau.
Diet Plan Example to Gain Muscle
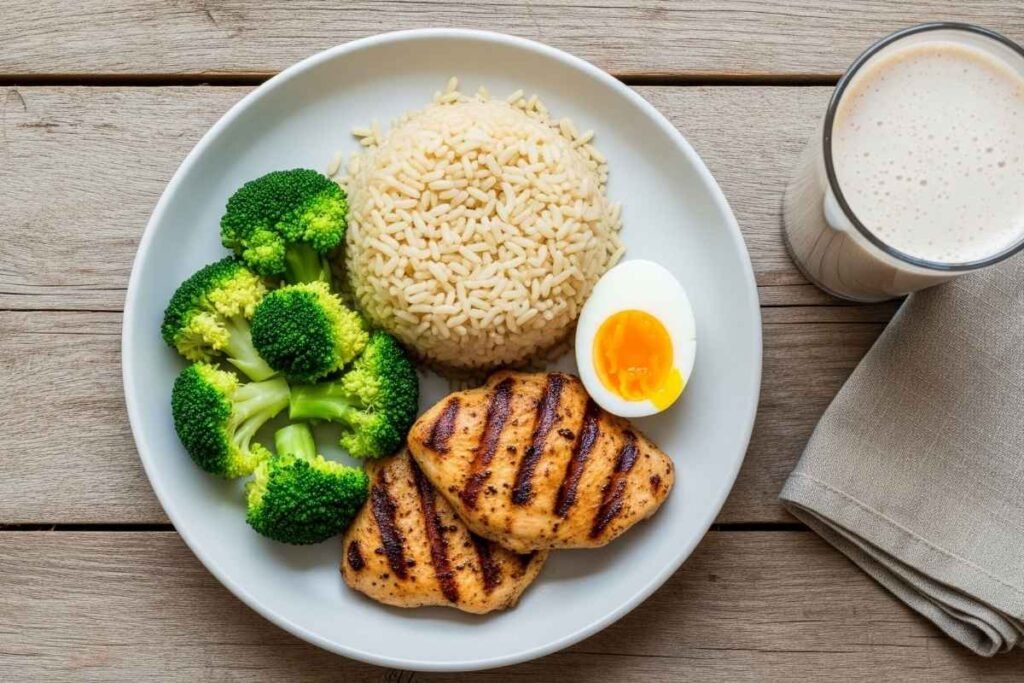

Meal 1 (Breakfast): Oats + 3 eggs + 1 banana
Meal 2 (Snack): Greek yogurt + almonds
Meal 3 (Lunch): Chicken breast + brown rice + vegetables
Meal 4 (Pre-Workout): Rice cake + peanut butter + whey protein
Meal 5 (Post-Workout): Whey shake + banana
Meal 6 (Dinner): Salmon + quinoa + broccoli
Meal 7 (Snack): Cottage cheese + berries
This plan ensures optimal nutrition timing, macronutrient balance and a steady caloric surplus.
Training Regimen Example

Monday – Push (Chest, Shoulders, Triceps)
Tuesday – Pull (Back, Biceps)
Wednesday – Legs
Thursday – Rest or Active Recovery
Friday – Upper Body Focus
Saturday – Lower Body + Core
Sunday – Rest
Each session should include 4–6 exercises, mixing compound and isolation movements with high workout intensity.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping progressive overload
- Not eating enough calories or protein
- Overtraining without enough recovery
- Doing too much cardio
- Ignoring form and proper technique
- Not sleeping enough
Fixing these issues can accelerate your gains.
Conclusion
To gain muscle, you need more than just lifting weights. It is a full body strategy that includes smart training, correct nutrition, quality sleep and consistent tracking. Focus on building strength, fueling your body and giving your muscles time to grow.
With the right training regimen, dedication and patience, you’ll see progress. Don’t chase shortcuts, master the basics and watch your body transform.
FAQs
How long does it take to gain noticeable muscle?
You may see changes in 4–8 weeks with proper training and diet. Full transformation can take months.
Do I need supplements to gain muscle?
Not necessarily. Real food is enough, but supplements like whey protein and creatine can help.
Can I gain muscle and lose fat at the same time?
Yes, especially for beginners. This requires precise nutrition and a structured workout plan.
How many times should I train per week?
3–6 sessions per week are ideal, depending on your fitness level and recovery.
Is soreness a sign of muscle growth?
Not always. Soreness can mean new stimulus, but not necessarily growth. Consistency and progression matter more.
Should I eat before or after workouts?
Both are important. Eat pre workout for energy and post workout for recovery and protein synthesis.






