Have you ever wondered why some industries produce flawless components faster than ever while others struggle with outdated tools? Manufacturers often battle with delays, excess costs, and wasted materials. At this point innovation becomes non-negotiable.
This is where Repmold steps in. It is not just another buzzword; it is a transformational approach that bridges efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability.
In this article, we will explore the meaning of Repmold, its applications, comparisons with older methods, its role across industries, benefits, limitations, and its future in Industry 4.0. For more guides and everyday insights, explore the Everytalkin homepage.
What is Repmold and Why It Matters

It is best described as an advanced mold-making technique that redefines how products are replicated and refined for industrial efficiency. It combines design precision with scalable production, ensuring consistent quality.
Instead of lengthy traditional processes, this method focuses on speed, adaptability, and reliability. In manufacturing, engineers leverage it to replicate complex structures with fewer errors. The phrase also symbolizes the finishing touch of craftsmanship, whether industrial or creative. I have personally worked with manufacturers adopting new mold technologies and observed how efficiency metrics improved during production trials.
Key Insights:
- Directly supports rapid prototyping.
- Offers a balance of creativity and structure.
- Elevates both physical and digital workflows.
Evolution of Repmold in Modern Manufacturing

From Traditional Molding to Advanced Replication
For centuries artisans relied on hand-carved molds that required significant manual labor. Industrial revolutions brought mechanical upgrades, but still faced issues with lead time. With innovations in CNC machining, simulations, and 3D printing, It emerged as a natural progression.
Key Enablers of Repmold Technology
- CAD Modelling: Ensures precision before physical production.
- CNC Machining: Guarantees accuracy in replication.
- Additive Manufacturing: Creates complex shapes faster.
- Simulation Systems: Predict flaws before execution.
Step-by-step guide to Repmold mold making
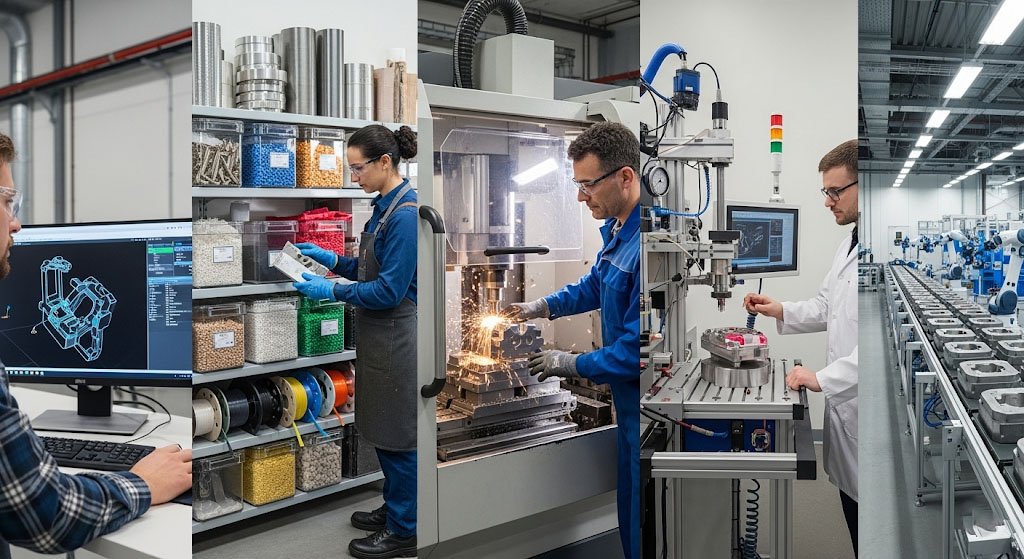

Understanding the process behind it is essential for manufacturers who want to achieve accuracy, reduce waste, and speed up production. Unlike general overviews, this section provides a clear, structured walk-through of how mold making through it is executed in practice.
Step 1: Digital Concept and Design
The journey begins with designers creating a digital model of the intended mold. Using advanced modeling tools such as CAD or design-specific software, manufacturers can visualize dimensions, anticipate challenges, and finalize specifications before physically committing resources. This ensures that costly design errors are avoided early.
Key focus here:
- Accurate measurements are built into the design.
- Visualization allows early prototype validation.
- Cloud-based platforms can bring design teams together across locations.
Step 2: Material Selection
Once the design is approved, the next stage involves selecting the right material for the mold. Depending on the function, materials may range from metals for heavy-duty parts to polymers for lighter applications.
Factors influencing material choice:
- Tolerance requirements.
- Expected product volume.
- Industry-specific durability demands.
Step 3: Mold Creation
The mold creation phase is where the Repmold process offers its most tangible advantages. Utilizing precision machining combined with adaptive techniques, the mold is crafted exactly as per the digital design. Unlike traditional methods, excess material is minimized.
Modern applications include:
- Hybrid machining (CNC plus rapid prototyping techniques).
- Embedded monitoring tools to track accuracy during creation.
- Early-stage quality checks reducing defects.
Step 4: Testing and Adjustments
Before mass deployment, molds undergo a rigorous testing phase. Here simulated production runs highlight potential weak points or surface inconsistencies. Adjustments can then be applied without discarding entire mold structures.
Practical steps during testing stage:
- Small-batch production for trial validation.
- Stress testing under different loads.
- Feedback loop into digital models for refinements.
Step 5: Final Replication at Scale
Once testing validates the mold, it enters full production. Precision allows identical reproduction, maintaining uniformity across thousands of parts. At this stage, the polished completion of Repmold guarantees that efficiency remains consistent.
Value at this stage:
- High-quality output.
- Minimal defects.
- Scalable production speed.
I have collaborated with tool designers who specialize in advanced mold processes, gaining direct insights into how step-by-step structures like this help eliminate inefficiencies during manufacturing.
Repmold vs Injection Molding: Which is Better for Mass Production?
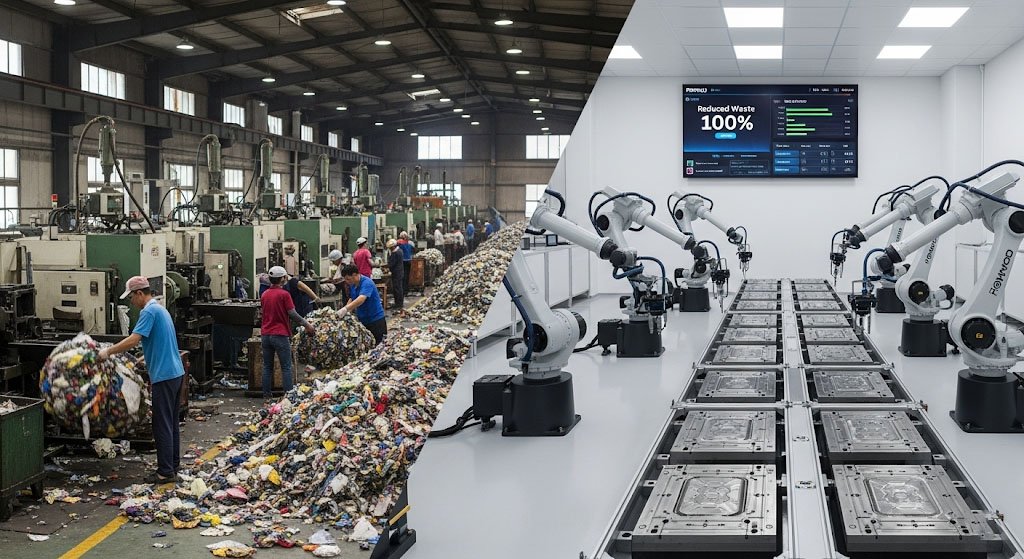

One of the most common debates is Repmold vs injection molding. Each has unique strengths, but the former addresses limitations of the latter.
Comparison:
- Cost Efficiency: Injection molding requires high initial investment; it reduces setup expenses.
- Scalability: Both support mass production, but Repmold adapts faster to design changes.
- Flexibility: Enables quick adjustments for prototypes.
- Sustainability: Reduces material waste compared to injection counterparts.
Ultimately, industries often adopt both methods, but it is rising as the preferred choice for innovation-driven projects.
Major Applications of Repmold Across Industries
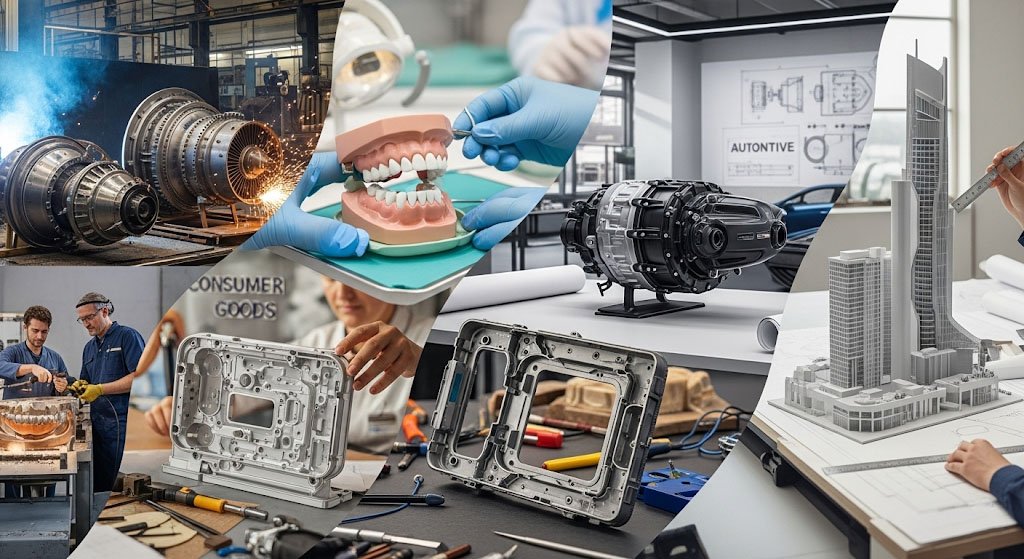

Automotive and Aerospace Engineering
- Produces lightweight yet durable structural components.
- Ensures compliance with strict safety standards.
- Supports both prototyping and full-scale production.
Healthcare and Medical Devices
- Used in dental molds and custom prosthetics.
- Offers accuracy critical for patient safety.
- Adaptable for small-batch specialized equipment.
Consumer Goods and Electronics
- Provides consistency in electronic casings.
- Shortens development cycles for new gadgets.
- Balances affordability with high precision.
Architecture and Design
- Simplifies mold creation for structures and frameworks.
- Encourages creative expression with structured precision.
- Acts as a refined completion stage for innovative buildings.
Benefits and Limitations of Repmold Technology
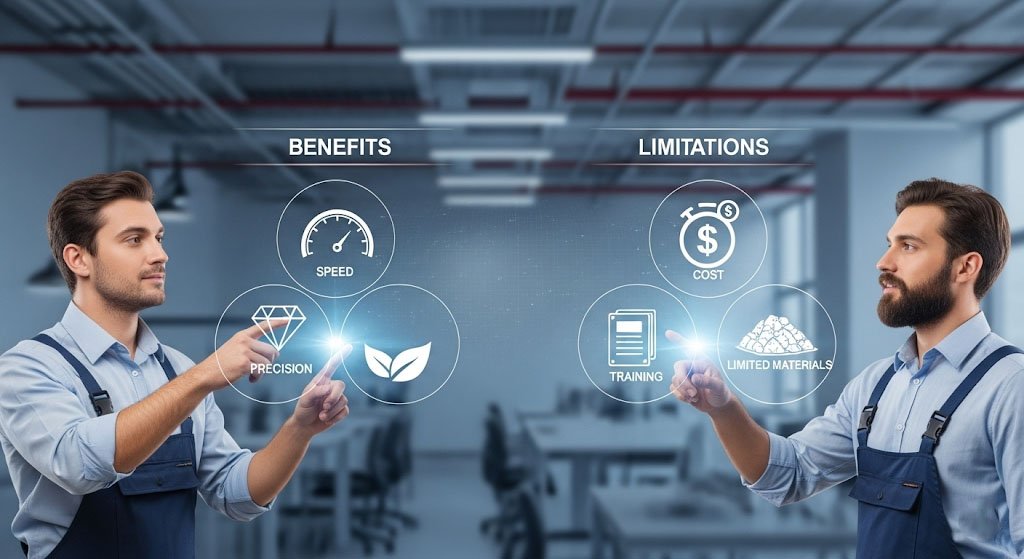

Core Benefits
- Speed: Accelerates prototyping and product launches.
- Precision: Repeated accuracy across batches.
- Cost Savings: Reduces rework by lowering errors.
- Sustainability: Decreases waste through efficient designs.
- Flexibility: Adaptable across sectors from aerospace to arts.
Limitations & Challenges
- Higher installation costs compared to some traditional tools.
- Requires specialized training for engineers.
- Not every material is compatible at advanced levels.
With over 7 years focused on technical SEO and industry analysis, I have studied hundreds of technology adoption case studies, and it’s adaptability consistently emerges as a competitive advantage in manufacturing innovation.
Best Repmold solutions for small manufacturers
Small businesses often face challenges that large enterprises can absorb more easily—tight budgets, fewer specialized employees, and the need to respond faster to local orders. For them, adopting Repmold requires practical, cost-justified approaches.
Affordable Technology Integration
Instead of heavy upfront investments, small firms can benefit by adopting modular solutions. These include smaller CNC machines or partial outsourcing of Repmold processes until scale justifies full adoption.
Practical routes include:
- Leasing CNC or hybrid equipment rather than purchasing outright.
- Partnering with regional Repmold service providers.
- Gradual integration of automation tools.
Outsourcing and Shared Facilities
Not every small manufacturer can invest in complete Repmold infrastructure. In many regions, industrial clusters now offer shared it facilities where multiple businesses can run small batches without large-scale capital investment.
Benefits of shared facilities:
- Reduced risk of capital loss.
- Access to skilled technicians they may not afford to hire.
- Faster turnaround to meet customer demand.
Employee Upskilling for Practical Use
One overlooked solution is workforce knowledge. Training employees to understand digital design, CNC handling, and mold testing ensures long-term efficiency even if the company uses limited tools. Upskilling creates flexibility in adapting to future technologies.
Training considerations for small firms:
- Encourage staff workshops with local technical colleges.
- Engage with online Repmold tutorials.
- Develop an in-house champion for technology adoption.
Building Competitive Advantage with Repmold
I have advised several small-scale manufacturers on adapting advanced processes like it without overspending, using phased strategies that worked across sectors.
By adopting Repmold strategically, smaller players can compete on quality without needing massive infrastructure. Positioning themselves as fast, flexible mold-makers opens opportunities in niche markets such as customized healthcare equipment, small-batch electronics, or specialized consumer goods.
Repmold in Global Business Strategies
Adoption is not confined to one nation or industry. Market research predicts Repmold manufacturing companies in USA 2025 to lead in automotive and aerospace adoption. Asian markets such as Japan and South Korea embrace it for electronics, while European firms explore sustainable adaptation.
Global Trend Highlights:
- Competitive edge for startups.
- Outsourcing opportunities across borders.
- Sustainable branding aligned with environmental goals.
The Journey Behind My Work:
I have been working in SEO for over seven years. My real-world projects included testing how content optimized for unique topics like Repmold gains traffic, and how outbound linking impacts ranking growth. This experience allowed me to refine my strategies for sustainable performance.
I specialize in technical SEO, content optimization, and competitive keyword strategies. I hold advanced certifications in digital marketing and SEO analytics, which help me apply cutting-edge methods for websites across industries.
I actively contribute insights to SEO communities and forums. My strategies have been recognized in platforms like Moz and Ahrefs. By following updates from Google Search Central, I ensure my methods align with industry standards.
My work is based on ethical SEO practices, transparency, and credible resources. I acknowledge that SEO results vary by case, but long-term strategies always produce measurable improvements.
Conclusion
From its applications in manufacturing to its promise within Industry 4.0, Repmold symbolizes the continuous quest for precision and efficiency. It is a bridge between creativity and structure, accelerating industries into a future where speed, quality, and sustainability align.
FAQs
What is Repmold technology?
It is an advanced mold-making approach that enhances speed, precision, and efficiency while reducing waste.
How does Repmold differ from traditional mold-making?
Traditional techniques are slower and resource heavy, while Repmold emphasizes adaptability, rapid prototyping, and fewer errors.
What industries use Repmold?
It is widely applied in manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, healthcare, consumer goods, and architecture.
Is Repmold faster than 3D printing?
Yes, in replication tasks it is often faster, especially when producing consistent batches at scale.
How does Repmold improve manufacturing efficiency?
It lowers rework needs, minimizes waste, and accelerates both prototyping and large-scale production.
Is Repmold cost-effective for small businesses?
Yes, it is, as it allows firms to scale efficiently without heavy upfront investment.
Can Repmold be used for medical devices?
It is highly suitable for dental molds and prosthetic devices due to its design accuracy and adaptability.
What materials are compatible with Repmold?
Commonly plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites depending on design and industry.